Enterprises are seeking a secure monitoring solution that performs encapsulation. Encapsulated Remote SPAN (ERSPAN) identifies visibility gaps and vulnerabilities, but using it enables flow data to passively monitor on one or more ports or VLANs, and then sends traffic to the target destination. ERSPAN transports mirrored traffic over an IP network and ensures better network reliability and availability.
What is ERSPAN?
According to Cisco’s documentation, it is “available only to Catalyst 6500, 7600, Nexus, and ASR 1000 platforms to date. The ASR 1000 supports ERSPAN source (monitoring) only on Fast Ethernet, Gigabit Ethernet, and port-channel interfaces.”
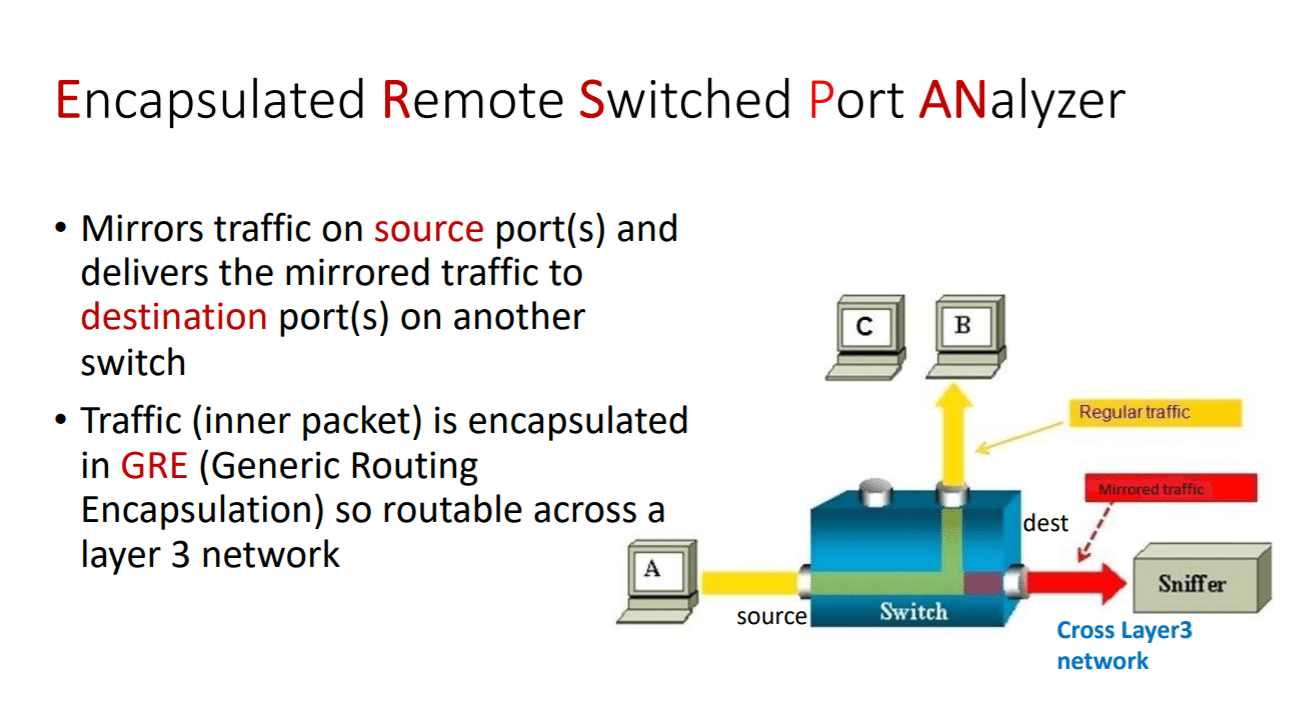
As deployments become more complex with virtualization, security platforms views have become fragmented, which compromises the integrity of network assets. ERSPAN enables you to mirror traffic from one or more source ports on a virtual switch, physical switch, or router. Then it sends the traffic to a destination IP host running PVS. Using ERSPAN, enterprises can overcome issues with getting network traffic copied in cloud environments. For example, VMware vSphere Distributed Switch (VDS) supports industry-standard features, such as port mirroring and NetFlow.
ERSPAN enhances the visibility into encrypted traffic for custom applications such as:
- SSL/TLS Decryption
- Malware Detection
- (DLP) Data Loss Prevention
- Application Performance Monitoring
- Vulnerability Detection
- Cloud Services Monitoring
- Adaptive Packet Filtering
- Anomaly Detection

Why ERSPAN Promotes Enhanced Visibility
As the number of vulnerabilities increases with the applications developed, the visibility to detect these vulnerabilities becomes vital for both NetOps and SecOps.
Let’s take a look at cache poisoning attack. This type of attack involves the injection of malicious data into recursive DNS servers operated by internet service providers (ISPs). From a SecOps perspective, an attack of this measure would compromise tons of users’ data. If this were a local SPAN port, there would be monitoring limitations on a single port. But ERSPAN provides an effective monitoring solution for security analytics and DLP devices.
As another example, we’d assume Facebook is fully protected at the perimeter, but somehow they were breached. ERSPAN may have been an alternate solution with the implementation of a network monitoring platform. Using this vulnerability assessment would keep them proactive on application activity, but also protect the personal data at the perimeter.
The ingestion of flow and metadata on top of ERSPAN enhances lateral visibility and safeguards your network.
In order to configure ERSPAN, it must be routable across a layer 3 network between the “source” switch and the “destination” switch. Please reference this sample configuration for the Cisco Nexus 7000 Series:
monitor session 1 type erspan-source description ERSPAN direct to Sniffer PC erspan-id 3 # required, # between 1-1023 vrf default # required destination ip 10.1.x.x # IP address of Sniffer PC source interface port-channel1 both # Port(s) to be sniffed filter vlan 1000 # limit VLAN(s) (optional) no shut # enable monitor erspan origin ip-address 10.1.x.x global
If you need better visibility into your network, download Scrutinizer and be proactive on the latest threats.





