Many ISPs filter bogon connections because bogon IP addresses have no legitimate use. If you find a bogon or bogus IP address in your firewall logs, it is likely due to a misconfiguration or someone intentionally creating a bogon connection for malicious purposes. This blog provides guidance on how to detect bogon connections with Plixer Scrutinizer and potentially discover other vulnerabilities that would compromise an enterprise network environment.
What are bogon IP addresses?
Bogon IP addresses are Martian addresses used to describe IP packets on the public internet that appear to be from an area of the IP address space reserved, but are not yet allocated or delegated by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) or any of the Regional Internet Registries (RIR).
Why would SecOps need to track bogon connections?
Bogon IP addresses are valuable to hackers because the packets cannot associated with an actual host. Most routers are unable to examine the source IP address of a packet; all the router cares about is the destination IP address, so they will forward bogon packets to their destination. A bogon packet cannot be used to initiate and set up a TCP connection, but bogons can be used to launch TCP SYN attacks and are used in some DDoS attacks. As enterprises adjust to a new normal environment, SoC Analysts play a vital role in detecting bogon connections and associated vulnerabilities.
How to investigate a bogon IP address with Plixer Scrutinizer
Plixer Scrutinizer’s new machine learning and artificial intelligence capabilities can filter out specific threats through network modeling. This will be helpful to SoC analysts who want to investigate Bogon attempts and connections. In the image below, our ML/AI features have detected the Bogon Attempt and Bogon Connection. Let’s dive deeper into the policy to understand who the violator and who is the target:
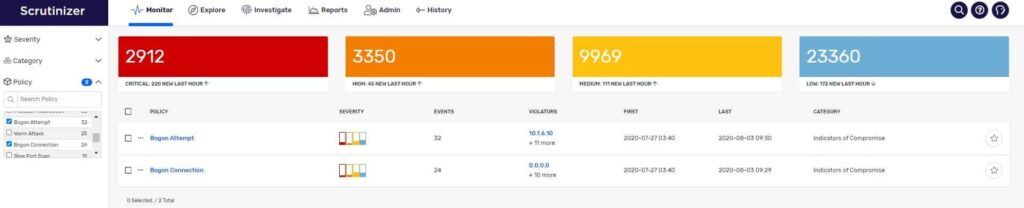
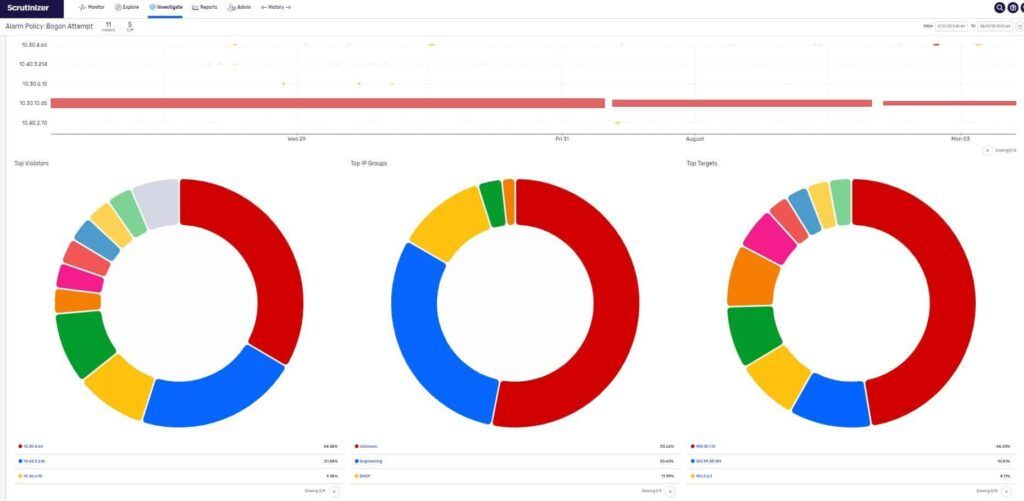
Plixer Scrutinizer can identify and align these multiple violators with specific groups and associated severe targets that would compromise the network as well. Once you click on the alarm policy, you’ll see that Scrutinizer has identified the top violators, top IP groups, and potential top targets associated with this alarm policy.
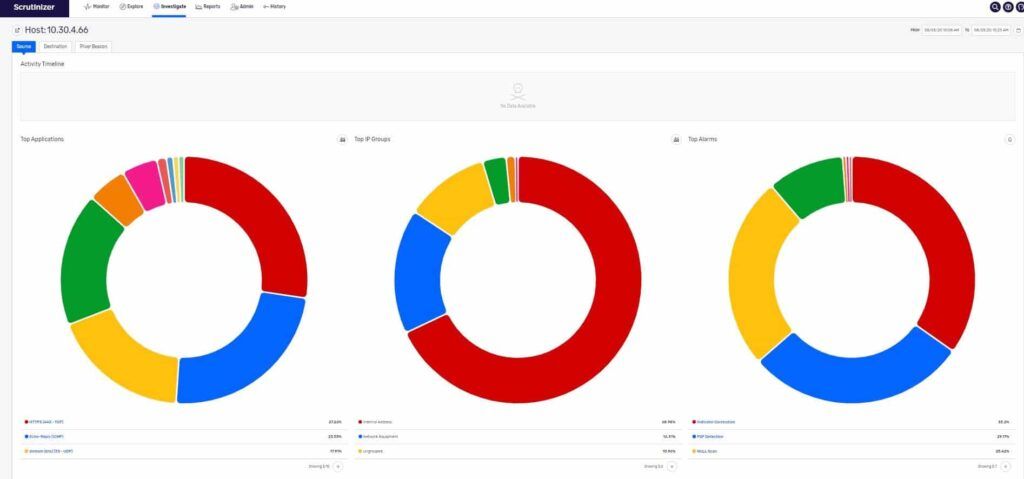
Below, Scrutinizer has identified the top Violator of the bogon attempt and found associated applications and alarm policies linked to this specific host as potential threats. Scrutinizer categorizes the host’s source and destination activity within the bogon alarm policy.
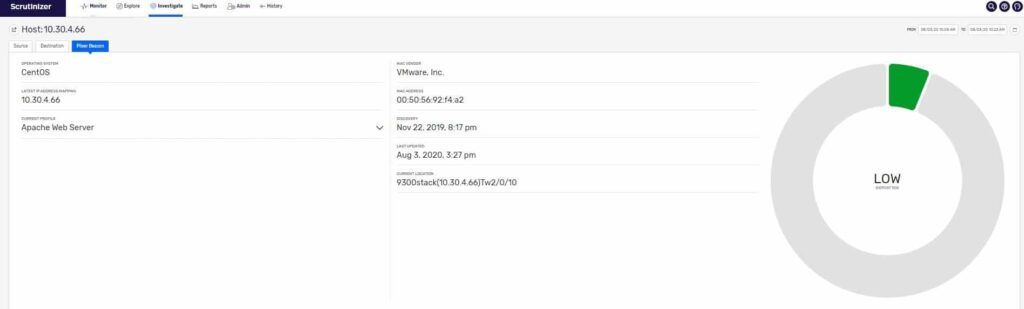
And by integrating Plixer Beacon with Scrutinizer, the SoC analyst take a step further and gain visibility and profiling of the actual host.
Let’s take an in-depth look at the Plixer Beacon integration. The profile of the endpoint shows the operating system, current IP address, device type, MAC address, and device location. This endpoint information is important when performing threat hunting because it reduces risk to the organization and enables SOC Analysts to proactively respond to incidents.
In my experience, having a network traffic analysis and network detection response system like Scrutinizer is extremely useful for proactively identifying and remediating bogon IP addresses.
Conclusion
If your team is seeking a solution to identify bogon connections in your infrastructure, please contact me and we can spin up an evaluation.


